A lot of people are always in a hurry these days. Have you ever stopped and taken a few moments to just look around and listen to the nature around you? Well, if you know me, I will stop mid-sentence to point out any bird that I see and hear. Birds are absolutely beautiful, smart, and innovative, especially when making a nest of their own. This job has given me the opportunity to be immersed not only in plants on a daily basis, but also in wildlife, most often, birds.
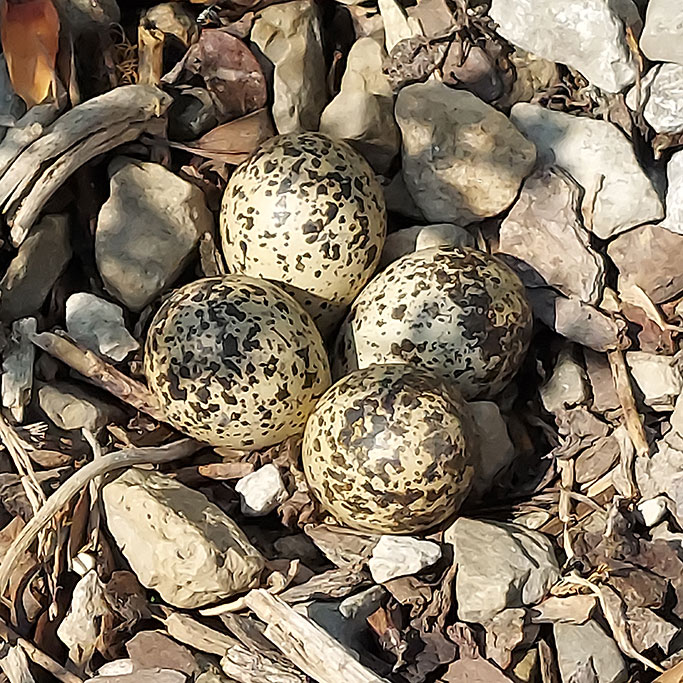

Here at Christensen’s, I’ve been lucky enough to see some stunning birds that either nest or stop by to visit the property. If you’ve been here you know our most common nesting bird is the killdeer who love to make their nests on the ground usually in rocky locations. If we’re being honest, this can sometimes be inconvenient to us. Regardless, we flag them off and give them space. Being able to watch these birds protect their eggs, and finally become parents to some of the cutest little birds I’ve ever seen is a very rewarding experience.

Cedar waxwings, a not-so-common bird even though they make Michigan their home all year long, also come to snack on the serviceberry trees along Gotfredson Road. These birds look like they have been painted by an amazing artist. A beautiful blend of grey, light brown, and yellow with a cool-looking black mask over their eyes make these birds a real sight to see.

One of my all-time favorite birds is the great blue heron. They come and fish out of our pond pretty much every day. They are mostly blue and grey with a bright orange and yellow bill, with long black plumes on their heads. When spotted flying you can see their long legs sticking out straight behind them, with a wide wingspan. Despite their size, they only weigh 5 to 6 pounds due to having hollow bones.

One of the rare sightings I’ve been lucky to see here is the majestic bald eagle. With a black/brown body accompanied by a white head and tail. These beauties soar through the air with wings flat (wingspan of about 7 feet), and heads extended far in front of their wings. Fun fact eagles can carry up to four times their body weight (they weigh 14 pounds).
These are just some of the birds that fly by or stop to visit us at Christensen’s. I love to be able to share these facts and pictures of some of my favorite birds with all of you. So, instead of rushing to get where you’re going, stop for a few moments and look around at the amazing wildlife that surrounds us. You just might be shocked at what you see. Nature is absolutely beautiful!