Kudzu – The Invasive Vine that Ate the South (or did it?)

Being from the North and a country music fan, I started hearing about Kudzu in songs by HARDY, Morgan Wallen, Alabama, Scotty McCreery and more. You can’t get far into country music before an artist compares something to the invasiveness of a Kudzu vine. My favorite being “My mama said addiction runs like a kudzu vine on our family tree…” Being in horticulture, I had to investigate this mythical beast of a plant and learn more about it.
Kudzu, or if we’re being scientific, Pueraria montana, was introduced at the 1876 World’s Fair Centennial Exhibition. Originally from Asia, it didn’t really make a splash with Americans. Farmers couldn’t figure out how to leverage the plant for any sort of profit and it was quickly gobbled up by grazing by livestock. It wouldn’t have actually taken off, if it wasn’t for a supplemented government program. It’s estimated that around 1945, there were about a million acres planted. That was a far cry from the 8 million acres the government hoped would be planted and the incentivization ended.
While the Kudzu on farms was plowed under or grazed away, the Kudzu on roadsides and railways grew to cover much of all the other vegetation, seemingly consuming the south at a rapid pace, up to a foot per day. This very visible conquest became the easy target of writers, poets and lyricists. This plant has taken on a cultural reference far surpassing most other southern plants. It has wrapped around the people to become an icon.

But in the end this plant doesn’t live up to the myth that’s been created around it. Horticulturists agree that it poses less of a threat than Asian privet, Japanese honeysuckle and invasive roses in the south. It does not grow inches in days and cover millions of acres. The U.S Forest service reports that in 2010 only 227,000 acres of forests are invaded by Kudzu. It sounds like a lot, but when you consider that over 1 million acres of the US are covered with Purple Loosestrife, you can see that it’s not nearly the problem we face from a local invasive species.
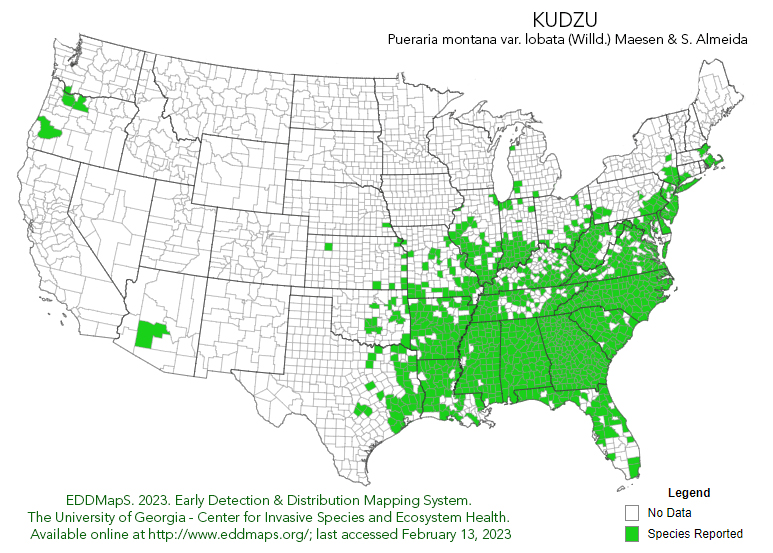
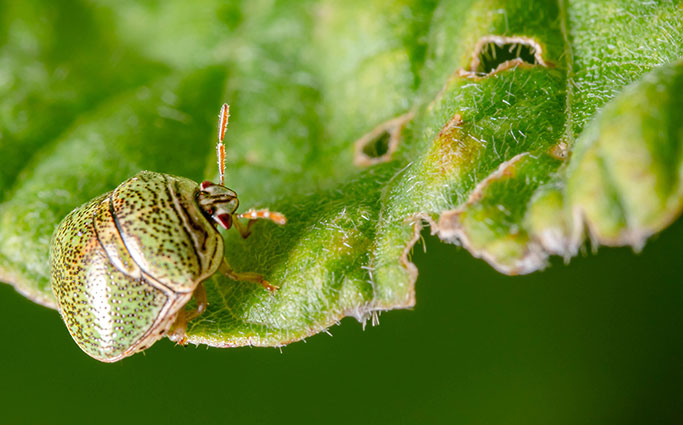
And some horticulturists even think it’s on the decline. It’s certainly debatable, but as many farming corporations, universities and the government have been attacking it with herbicides, mowers, fires, goats and replanting, it is possible that they are starting to get a handle on the spread. Another factor is the Japanese kudzu bug that has begun infesting large areas of kudzu and sucking the life out of the myth.

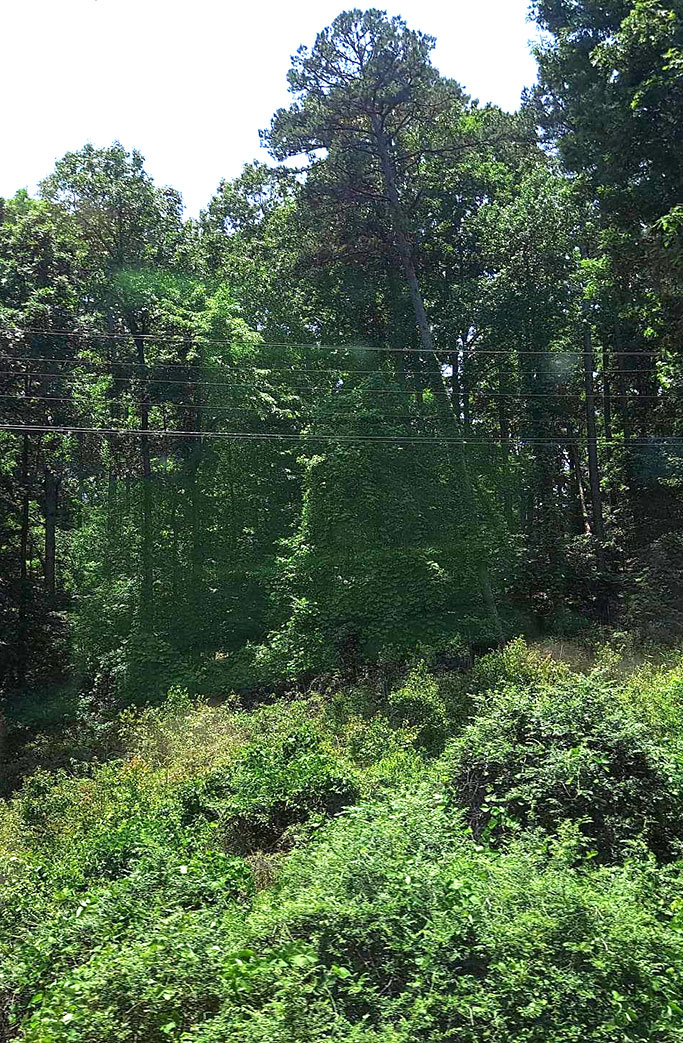
When traveling near Gatlinburg, Tennessee last year, I was able to see the monster for myself. It was certainly an overwhelming site on the side of the road creating a jungle-like look for expanses of the highway. I would never want to battle this vine in my yard. It was always assumed that Kudzu was contained by the cool temperatures of the north, but a recent study indicated that it can survive in subzero conditions. And with climates shifting and zones redefining, it’s actually getting closer to the northern states and the Midwest by the year. The romantic version of the plant in songs, poems and stories is a lot more palatable when it stays far away from my yard.
But whether you love it or hate it, at least you may know more about Kudzu than you did before. If you’re looking for additional information and articles, this is where I pulled the majority of my research from:

Kudzu’s Entanglement of South Begins to Unravel by Dan Chapman
WorldWideScience.org
